By Cali Storch
Category Archives: Language
Retracing my steps
By Alejandra Gorostiza
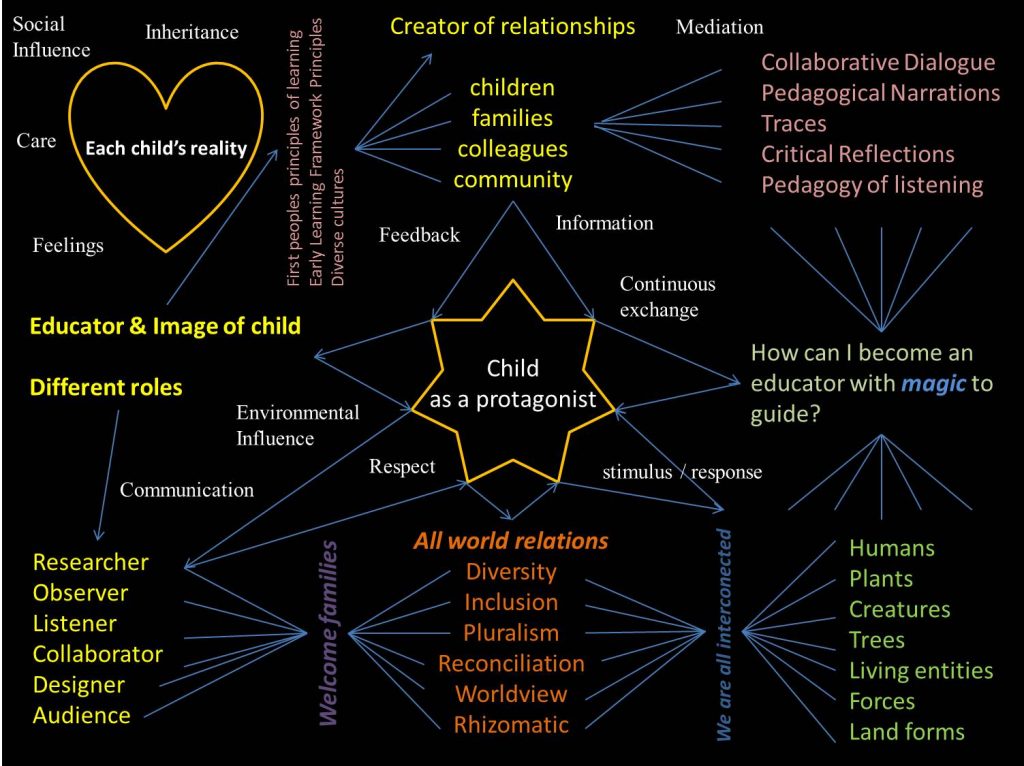
The Early Learning Framework (Government of BC, 2019) describes a rhizome as a plant that develops underground and buds in many directions and without a predictable pattern. Inspired by this image, I created this visual map of my learning connections on this wonderful, complex, and unpredictable path to becoming an early childhood educator.
Grateful for so much!
References:
Government of BC. (2019). British Columbia early learning framework. Victoria, BC: Queen’s Printer.
Collaborative Dialogue 2
Dear reader!
The following is a collective response to the second event in the ‘Collaborative Dialogue’ series, a professional development opportunity hosted on March 17, 2021. You will find a brief introduction to this series in our blog post posted on March 8th. We invited presenters, guests, and hosts to co-compose this blog post. Our hope was to sustain the ‘Collaborative Dialogue’ by staying with the generous offerings and creating a space for a playful “back and forth” (see Amanda Gillmore’s post, 2021). We created an online document that updates in real time, shared the invitation to contribute, and waited…
We are connecting to several blog posts shared at the ‘Collaborative Dialogue’:
Sabrina and Julie (forthcoming – on mentorship)
Amanda Gillmore (March 17, 2021)
Vania Zanetti (March 16, 2021)
Kate Boyd and Danielle Cazes (February 23, 2021)
Antje: Welcome to this site for curiosity, experimentation, improvisation, and wonder! You are invited to join this written dialogue inspired by the question: How might we – collectively – continue the ‘Collaborative Dialogue’ event(s) in a virtual way? Here are a few of my questions as a way to enter the conversation, feel free to add your own. What are you compelled to write about as you reflect about the event? What ideas and themes are you returning to? What are some of the alternate stories that you witnessed at the ‘Collaborative Dialogue’ event? What might this dialogue set into motion? What questions are you left with?
Cheryl: Amanda’s swinging boots are an invitation to a child who responds. What are the messages that we send to children, to the world in the way we move? What are the senses beyond words? Toddlers and educators take time to eat their snacks and linger with Sabrina and her mentor Julie. Conversations verbal and otherwise activated by the shared experience of nourishing our bodies and souls. What is activated between us as we think with Vania and Peter Moss?
Antje: I shared Vania’s reflections on play spaces with my sister when we visited Linley Valley Cottle Lake Park in Nanaimo. Inspired by Peter Moss, Vania “wonder[ed] about the multiple ways spaces can provoke exploration”. Their words echoed into this space. We lingered to watch my nephews with/in the trees and stream. This also takes me to Powell River, to the forest, just out of sight, that Kate and Danielle visit with children and their families. How might we cultivate a love for a place? What would the vocabulary be?

Vania: I had asked Sabrina and Julie to speak on their mutual connection to each other. In my reflections I wondered about my own mentor (twenty years ago). I asked myself the same question I asked during the dialogue. What was the moment when I knew I could trust or that I felt connected to my mentor? And I knew the answer. I’ve never forgotten the moment because I use the same words when I work with my colleagues to this day.
There are times for whatever reason when children will be resourceful in getting their needs met. On this particular day a child was not getting what they needed from me (a newbie). Clearly thinking I didn’t know what they were asking they moved on to make the same request from my mentor. My mentor had been an educator in the program for a few years more than myself. My mentor replied with “Vania is right…” and repeated what I had already told the child. Word for word. The child moved on satisfied with the response. To this day I don’t remember what the request was but those three words made me feel so validated, so able, so confident and so trusted. I felt connected knowing they were supporting me in a shared role of caregiver. This was a mentor that saw the importance of stability, consistency and predictability for both the child and a mentee’s emotional development.
Later that day we were able to discuss the moment together. I’m assuming we made changes as may have been needed or perhaps we laughed together at the child’s ingenuity. In reflection the connection happened because my mentor had been vulnerable with me. Not allowing the child to perceive them as ‘greater than’ in that moment made me feel I could be vulnerable together with them. The willingness to be vulnerable made way for connection and trust between us.
When I consider this I think again about the play spaces we create. If dominant language is used when choosing materials, choosing curriculums, and enforcing outcomes how can we be vulnerable with each other? How authentic are our connections with colleagues or the children we care for? How can growth happen when we are not able to make connections that help keep us open to new possibilities?
Reimagining Early Childhood Spaces
By Vania Zanetti
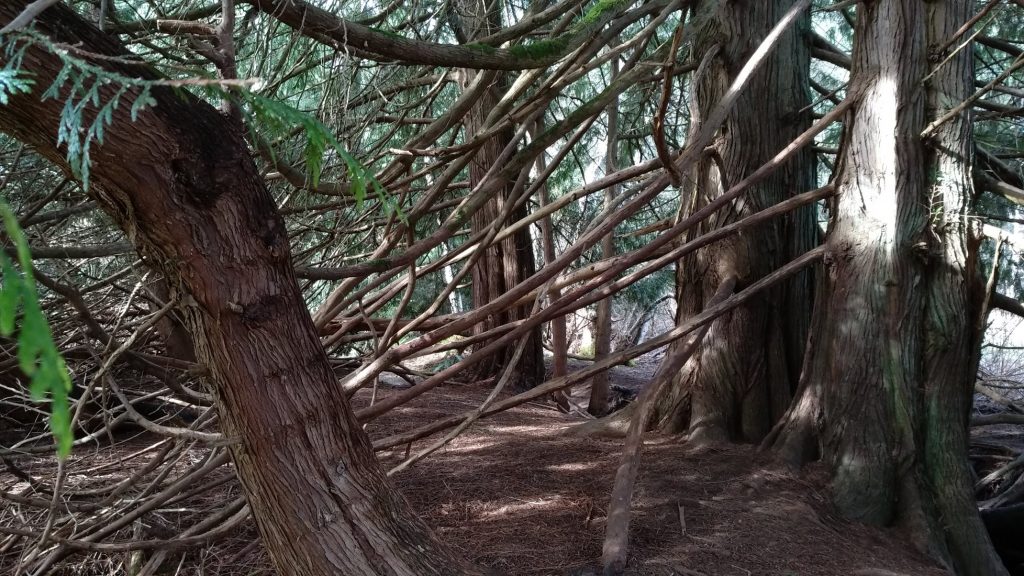
In the book Alternative Narratives in Early Childhood: An introduction for Students and Practitioners, Moss (2019) speaks to the idea that the vocabulary we use in early childhood spaces shapes early years practices and experiences. Moss suggests that the dominant language of the early years narrative is “instrumental, calculative and economistic, technical and managerial, dull and lifeless” (p. 81). This makes me thoughtful about theoretical influences that inform the choices that educators make and ultimately shape what is imagined for early childhood spaces.
With the image above I am intrigued to think about the language used to create environments for children. I imagine conversations about safety and regulations that stripped aged trees of lower branches to keep children from scaling higher than they “should”. I wonder, ‘How often, and why, are toys and equipment chosen in early childhood settings because they include words such as safety, quality, durability, and development?
As an alternative to the dominant narrative Moss offers the language used in Reggio Emilia. The language is almost dream-like with a narrative that uses words like exploration, possibility, imagination, and becoming. It makes me wonder about the multiple ways spaces can provoke exploration, project making, and pathways for growth and development. I’m curious about connections to the Early Learning Framework (Government of BC, 2019, p. 77) and welcome the invitation to engage with the critically reflective question, “What opportunities do children have to access materials that can be transformed or investigated?”
I wonder how we can nurture alternative dialogues about children’s spaces. How might these dialogues be informed by the first principle listed in the Early Learning Framework (Government of BC, 2019), “Children are strong, capable in their uniqueness, and full of potential” (p. 15)? What kinds of worlds might become possible?
References:
Government of British Columbia. (2019). British Columbia early learning framework (2nd ed.). Victoria: Ministry of Education, Ministry of Health, Ministry of Children and Family Development, & British Columbia Early Learning Advisory Group. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/education-training/early-learning/teach/early-learning-framework
Moss, P. (2019). Reggio Emilia: A story of democracy, experimentation, and potentiality. In Alternative narratives in early childhood: An introduction for students and practitioners (pp. 81). New York, NY: Routledge.
Becoming Co-teachers
By Antje Bitterberg and Summer Lin
In the Spring of 2020, soon after the announcement that most courses in post-secondary institutions would be moved online because of the pandemic, we had the opportunity of co-teaching a group of ECEC students from VIU’s Cowichan, Powell River, and Nanaimo campuses. With students from several communities, and the sudden shift from face-to-face classes to online classes, we wanted to focus on creating an online community for thinking and learning together. How might we cultivate collaborative, generative, and collegial modes of being teachers?
We welcomed the invitation to think together and found much joy in the process of becoming co-teachers. We oriented ourselves toward this process of creating a space for co-teaching. On a day-to-day basis we committed to teaching together. As colleagues, we actively resisted the lure of efficiency. We did not divide the work among ourselves evenly allowing us to get things done. Instead we made time to slow down and to begin our days with dialogue. As roommates on zoom we lived and breathed the course together.
In our daily conversations within the context of our course and beyond, we became curious about the power of language. We wondered, ‘How might language shape what is possible/ measurable/ observable/ visible/ valued in early childhood spaces?’ To think about/with language, we introduced the concept of binary (paired) oppositions, where “[e]ach word…relies for its meaning on the other. We need the word fat to define slim. The same is so for straight and gay, black and white, etc. A pair always has two” (MacNaughton, 2005, p. 62). We have included more pairs below, some are borrowed from Glenda MacNaughton, others we brainstormed with the students.
- complete/ incomplete
- predictable/ unpredictable
- normal/ abnormal
- boy/ girl
- developed/ underdeveloped
- rich/ poor
- efficient/ inefficient
It is important to note that these “pairs are always ranked, so one part of the pair always has higher value in the ranking and is privileged over the ‘other’. So, using binary oppositions places some meanings in a secondary, subordinate position and often an aberrant position” (Mac Naughton, 2005, p. 63). Mac Naughton (2005, p. 118) offers the following questions:
- “How does binary thinking enter your everyday discussions in early childhood studies?”
- “What is silenced or othered through the hierarchical thinking in these binaries?”
- “What everyday words could you put under erasure to help you wonder new meanings and actions for social justice in your classroom?”
Rejuvenated and transformed by our process of thinking together, we invite you to join us by sharing your (in)complete engagement with these questions, your own wonderings, or connections to the Early Learning Framework (Government of BC, 2019) by responding to this post!
References
Government of British Columbia. (2019). British Columbia early learning framework (2nd ed.). Victoria: Ministry of Education, Ministry of Health, Ministry of Children and Family Development, & British Columbia Early Learning Advisory Group. https://www2.gov.bc.ca/gov/content/education-training/early-learning/teach/early-learning-framework
Mac Naughton, G. (2005). Doing Foucault in early childhood studies: Applying poststructural ideas. Routledge.
